8 Spin as a consequence of a multi-valued phase
As shown by [5], [19], and others, spin in non-relativistic QT may be introduced in exactly the same manner as
the electrodynamic potentials. In this section we shall apply a slightly modified version of their method
and try to derive spin in an alternative way - which avoids the shortcoming mentioned in the last
section.
[5] and [19] introduce the potentials by applying the well-known minimal-coupling rule to the free Hamiltonian.
In the present treatment this is achieved by making the quantity 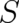 multi-valued. The latter approach seems
intuitively preferable considering the physical meaning of the corresponding classical quantity. Let us first review
the essential steps [see [32] for more details] in the process of creating potentials in the scalar Schrödinger
equation:
multi-valued. The latter approach seems
intuitively preferable considering the physical meaning of the corresponding classical quantity. Let us first review
the essential steps [see [32] for more details] in the process of creating potentials in the scalar Schrödinger
equation:
- Chose a free Schrödinger equation with single-valued state function.
- ’Turn on’ the interaction by making the state function multi-valued (multiply it with a multi-valued
phase factor)
- Shift the multi-valued phase factor to the left of all differential operators, creating new terms
(potentials) in the differential equation.
- Skip the multi-valued phase. The final state function is again single-valued.
Let us adapt this method for the derivation of spin (considering spin one-half only). The first and most
important step is the identification of the free Pauli equation. An obvious choice is
![[ ]
ℏ--∂-- --1--- ℏ---∂--- 2 ¯
+ ( ) + V ψ = 0,
i ∂ t 2m i ∂ ⃗x](stader432x.png) | (96) |
where 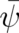 is a single-valued two-component state function; (96) is essentially a duplicate of Schrödinger’s
equation. We may of course add arbitrary vanishing terms to the expression in brackets. This seems trivial, but
some of these terms may vanish only if applied to a single-valued
is a single-valued two-component state function; (96) is essentially a duplicate of Schrödinger’s
equation. We may of course add arbitrary vanishing terms to the expression in brackets. This seems trivial, but
some of these terms may vanish only if applied to a single-valued 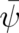 and may lead to non-vanishing
contributions if applied later (in the second of the above steps) to a multi-valued state function
and may lead to non-vanishing
contributions if applied later (in the second of the above steps) to a multi-valued state function
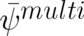 .
.
In order to investigate this possibility, let us rewrite Eq. (96) in the form
![[ ]
--1---⃗ ⃗ ¯
ˆp0 + ˆp ˆp + V ψ = 0,
2m](stader436x.png) | (97) |
where 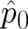 is an abbreviation for the first term of (96) and the spatial derivatives are given by
is an abbreviation for the first term of (96) and the spatial derivatives are given by
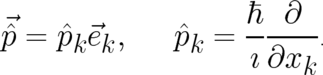 | (98) |
All terms in the bracket in (97) are to be multiplied with a 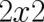 unit-matrix
unit-matrix 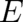 which has not be written
down. Replace now the derivatives in (97) according to
which has not be written
down. Replace now the derivatives in (97) according to
 | (99) |
where 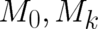 are hermitian
are hermitian 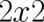 matrizes with constant coefficients, which should be constructed
in such a way that the new equation agrees with (97) for single-valued
matrizes with constant coefficients, which should be constructed
in such a way that the new equation agrees with (97) for single-valued 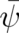 , i.e. assuming the validity of the
condition
, i.e. assuming the validity of the
condition
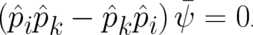 | (100) |
This leads to the condition
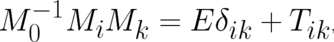 | (101) |
where 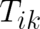 is a
is a 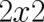 matrix with two cartesian indices
matrix with two cartesian indices 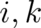 , which obeys
, which obeys 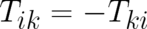 . A
solution of (101) is given by
. A
solution of (101) is given by 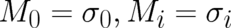 , where
, where 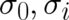 are the four Pauli
matrices. In terms of this solution, Eq. (101) takes the form
are the four Pauli
matrices. In terms of this solution, Eq. (101) takes the form
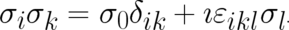 | (102) |
Thus, an alternative free Pauli-equation, besides (96) is given by
![[ ]
( )2
ℏ ∂ 1 ℏ ∂ ∂
------ + ------ --- σ -----σ -------+ V ψ¯ = 0.
i k
i ∂ t 2m i ∂ xi ∂ xk](stader454x.png) | (103) |
The quantity in the bracket is the generalized Hamiltonian constructed by [5] and [19]. In the present approach
gauge fields are introduced by means of a multi-valued phase. This leads to the same formal consequences as the
minimal coupling rule but allows us to conclude that the second free Pauli equation (103) is more
appropriate than the first, Eq. (96), because it is more general with regard to the consequences of
multi-valuedness. This greater generality is due to the presence of the second term on the r.h.s.
of (102).
The second step is to turn on the multi-valuedness in Eq. (103), 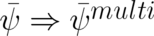 , by multiplying
, by multiplying 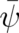 with a multi-valued two-by-two matrix. This matrix must be chosen in such a way that the remaining steps
listed above lead to Pauli’s equation (93) in presence of an gauge field. Since in our case the final result (93) is
known, this matrix may be found by performing the inverse process, i.e. performing a singular gauge
transformation
with a multi-valued two-by-two matrix. This matrix must be chosen in such a way that the remaining steps
listed above lead to Pauli’s equation (93) in presence of an gauge field. Since in our case the final result (93) is
known, this matrix may be found by performing the inverse process, i.e. performing a singular gauge
transformation 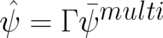 of Pauli’s equation (93) from
of Pauli’s equation (93) from 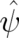 to
to 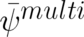 , which removes
all electrodynamic terms from (93) and creates Eq. (103). The final result for the matrix
, which removes
all electrodynamic terms from (93) and creates Eq. (103). The final result for the matrix 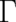 is given
by
is given
by
![∫
x,t [ ]
-e-- ′ ′ ′ ′ ′ ′
Γ = E exp {i dx kAk (x , t ) - cdt ϕ (x , t ) },
ℏc](stader461x.png) | (104) |
and agrees, apart from the unit matrix 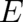 , with the multi-valued factor introduced previously [see (17)
and (52)] leading to the electrodynamic potentials. The inverse transition from (103) to (93),
i.e. the creation of the potentials and the Zeeman term, can be performed by using the inverse
of (104).
, with the multi-valued factor introduced previously [see (17)
and (52)] leading to the electrodynamic potentials. The inverse transition from (103) to (93),
i.e. the creation of the potentials and the Zeeman term, can be performed by using the inverse
of (104).
The Hamiltonian (103) derived by [5] and [19] shows that spin can be described by means of the same abelian
gauge theory that leads to the standard quantum mechanical gauge coupling terms; no new adjustable fields or
parameters appear. The only requirement is that the appropriate free Pauli equation (103) is chosen as starting
point. The theory of [12], on the other hand, started from the alternative (from the present point of view
inappropriate) free Pauli equation (96) and leads to the conclusion that spin must be described by a non-abelian
gauge theory.
As far as our derivation of non-relativistic QT is concerned we have now two alternative, and in a sense
complementary, possibilities to introduce spin. The essential step in the second (Arunsalam-Gould) method is
the transition from (96) to the equivalent free Pauli equation (103). This step is a remarkable short-cut for the
complicated calculations, performed in the last section, leading to the various terms required by the principle of
minimal Fisher information. The Arunsalam-Gould method is unable to provide the shape (95) of
the corresponding macroscopic forces but is very powerful insofar as no adjustable quantities are
required. It will be used in the next section to perform the transition to an arbitrary number of
particles.
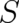 multi-valued. The latter approach seems
intuitively preferable considering the physical meaning of the corresponding classical quantity. Let us first review
the essential steps [see [32] for more details] in the process of creating potentials in the scalar Schrödinger
equation:
multi-valued. The latter approach seems
intuitively preferable considering the physical meaning of the corresponding classical quantity. Let us first review
the essential steps [see [32] for more details] in the process of creating potentials in the scalar Schrödinger
equation:
![[ ]
ℏ--∂-- --1--- ℏ---∂--- 2 ¯
+ ( ) + V ψ = 0,
i ∂ t 2m i ∂ ⃗x](stader432x.png)
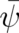 is a single-valued
is a single-valued 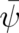 and may lead to non-vanishing
contributions if applied later (in the second of the above steps) to a multi-valued state function
and may lead to non-vanishing
contributions if applied later (in the second of the above steps) to a multi-valued state function
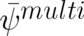 .
.
![[ ]
--1---⃗ ⃗ ¯
ˆp0 + ˆp ˆp + V ψ = 0,
2m](stader436x.png)
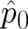 is an abbreviation for the first term of (
is an abbreviation for the first term of (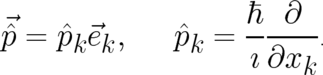
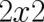 unit-matrix
unit-matrix 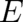 which has not be written
down. Replace now the derivatives in (
which has not be written
down. Replace now the derivatives in (
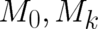 are hermitian
are hermitian 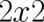 matrizes with constant coefficients, which should be constructed
in such a way that the new equation agrees with (
matrizes with constant coefficients, which should be constructed
in such a way that the new equation agrees with (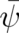 , i.e. assuming the validity of the
condition
, i.e. assuming the validity of the
condition
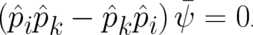
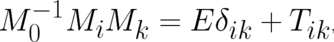
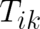 is a
is a 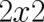 matrix with two cartesian indices
matrix with two cartesian indices 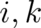 , which obeys
, which obeys 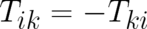 . A
solution of (
. A
solution of (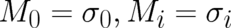 , where
, where 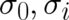 are the four Pauli
matrices. In terms of this solution, Eq. (
are the four Pauli
matrices. In terms of this solution, Eq. (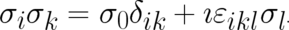
![[ ]
( )2
ℏ ∂ 1 ℏ ∂ ∂
------ + ------ --- σ -----σ -------+ V ψ¯ = 0.
i k
i ∂ t 2m i ∂ xi ∂ xk](stader454x.png)
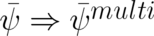 , by multiplying
, by multiplying 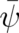 with a multi-valued two-by-two matrix. This matrix must be chosen in such a way that the remaining steps
listed above lead to Pauli’s equation (
with a multi-valued two-by-two matrix. This matrix must be chosen in such a way that the remaining steps
listed above lead to Pauli’s equation (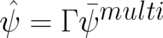 of Pauli’s equation (
of Pauli’s equation (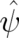 to
to 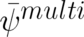 , which
, which 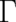 is given
by
is given
by
![∫
x,t [ ]
-e-- ′ ′ ′ ′ ′ ′
Γ = E exp {i dx kAk (x , t ) - cdt ϕ (x , t ) },
ℏc](stader461x.png)
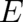 , with the multi-valued factor introduced previously [see (
, with the multi-valued factor introduced previously [see (